
Building an Effective B2B Sales Process: A Comprehensive Guide
Feb 23, 2026
Feb 23, 2026

Alex Zlotko
CEO at Forecastio
Last updated
Feb 23, 2026
Reading time
15 min
Share:
Share
Automate your B2B sales process with Forecastio

Introduction
The B2B sales process has evolved significantly in recent years, driven by more informed potential buyers, extended sales cycles, and increasing market competition. Today’s sales teams must navigate a complex buying process where decision-makers scrutinize every investment, making it essential to adopt a structured sales process that improves efficiency and boosts sales performance.
With tighter budgets and a growing emphasis on measurable ROI, businesses can no longer afford a disorganized selling process. A defined sales process helps sales reps identify and engage high-quality leads, manage the sales funnel effectively, and guide potential clients through the customer journey with precision. By implementing a well-defined sales process, organizations can optimize their sales efforts, increase customer satisfaction, and consistently meet sales targets.
In this article, we’ll explore the key sales process stages, best practices for sales professionals, and actionable strategies for building an effective sales process that accelerates revenue growth and improves deal closing.
What Is a B2B Sales Process?
A B2B sales process is a structured sales process that outlines a clear sequence of steps for sales teams to follow when converting high-quality leads into paying customers. This defined sales process ensures consistency, enhances sales performance, and provides a scalable framework for sales organizations to drive revenue growth.
A well-defined sales process is essential for navigating the complexities of the buyer's journey, especially in B2B environments where multiple stakeholders are involved in the buying process. By aligning sales process stages with customer relationship management best practices, businesses can improve customer satisfaction, optimize sales efforts, and increase their chances of closing deals efficiently.
An effective sales process not only standardizes sales activities but also empowers sales reps with the right sales tools, data, and strategies to engage potential clients at the right time. By adopting a structured approach, sales and marketing teams can better manage the sales funnel, refine their sales pitch, and maximize conversions. And when combined with modern approaches like AI-driven analytics and machine learning sales forecasting, companies gain even deeper insights into pipeline health and future revenue potential.
The Difference Between a Sales Process and a Buying Process
A sales process and a buying process may seem similar, but they represent two distinct perspectives in B2B sales. The sales process is the structured approach that sales teams follow to convert potential customers into buyers, while the buying process (also referred to as the buyer’s journey) focuses on how decision-makers and multiple stakeholders evaluate, compare, and ultimately choose a solution that meets their needs.
Understanding both the sales process and the buying process is crucial because modern B2B buyers are more independent and research-driven than ever before. Today’s sales professionals must go beyond traditional cold calling and scripted sales pitches—they need to engage with potential buyers at the right moments.
By aligning the sales process stages with the buyer's journey, sales teams can increase their chances of closing deals, improve sales performance, and provide a seamless experience that leads to higher customer satisfaction.
Supercharge your growth with our expertly crafted sales improvement strategies, featuring actionable tactics to boost conversions and accelerate pipeline success.
Sales Process vs. Buying Process
To create an effective sales process, it’s essential to recognize how each stage corresponds to the buyer’s decision-making journey. Below is a comparison of the structured sales process and the buying process:
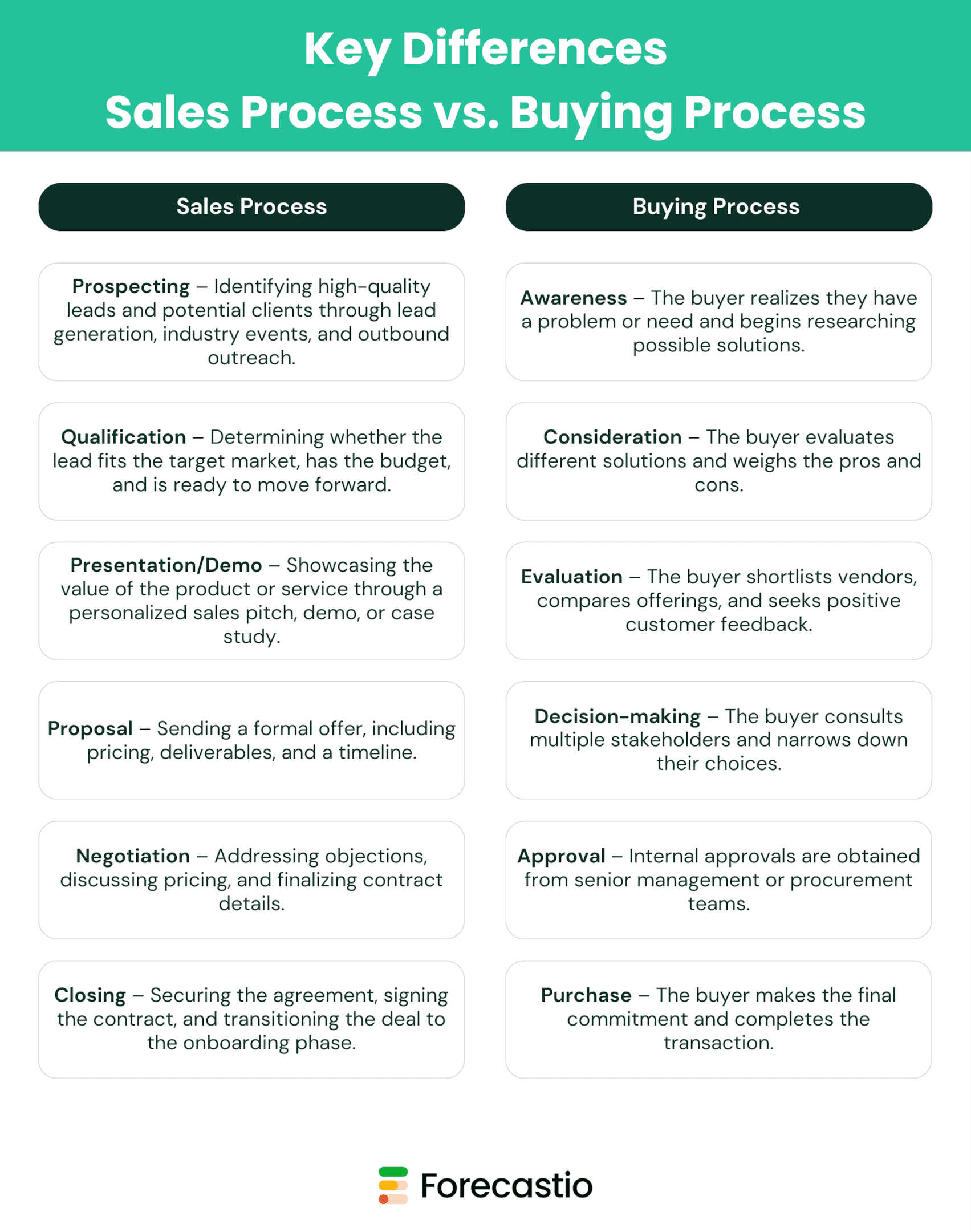
Why Sales Teams Must Align with the Buyer’s Journey
The most successful sales processes are not rigid checklists but adaptable frameworks that align with the buying process. A well-defined sales process ensures that sales reps engage buyers at the right time with relevant messaging, making it easier to guide them through the sales funnel.
By understanding how B2B buyers progress from awareness to purchase, sales leaders can refine their sales strategies, personalize their approach, and build long-term customer relationships that drive revenue growth.
Why an Effective Sales Process Is Important
A well-defined sales process is the foundation of a high-performing sales organization. It provides structure, clarity, and consistency, ensuring that sales reps follow a repeatable approach that maximizes efficiency and improves sales performance.
By implementing an effective sales process, businesses can achieve:
1. Increased Efficiency
A structured sales process helps sales reps focus their sales efforts on high-quality leads, reducing wasted time on low-probability opportunities. By clearly defining sales process stages, reps know exactly when to engage potential customers, how to qualify leads effectively, and which actions will move deals through the sales funnel.
2. Improved Sales Forecasting
A defined sales process creates consistency in sales activities, making it easier for sales leaders and sales managers to predict outcomes with greater accuracy. Reliable sales forecasting enables companies to set realistic sales targets, allocate resources effectively, and anticipate revenue fluctuations. By tracking key performance metrics across the sales cycle, organizations can optimize strategies and make data-driven decisions.
3. Stronger Sales Enablement & Training
For new sales reps, a well-defined sales process serves as a roadmap to success. By following a sales playbook, reps can ramp up faster, understand best practices, and execute proven sales techniques. A structured framework also enhances sales training, equipping teams with the right sales tools to engage potential clients, deliver compelling sales pitches, and navigate complex buying processes.
4. Higher Conversion Rates
An effective sales process ensures that each step is optimized for closing deals. By using a sales process-based approach, sales representatives can nurture potential buyers, overcome objections, and strategically guide them through the buyer's journey. A well-structured selling process reduces drop-off rates and improves the likelihood of successful deal closures.
5. Enhanced Customer Experience & Trust
Aligning sales efforts with customer relationship management best practices ensures that buyers feel supported, informed, and valued. A successful sales process is customer-centric, focusing on solving pain points, addressing concerns, and personalizing interactions. When sales professionals prioritize the needs of potential customers, they build stronger relationships, increase customer satisfaction, and boost long-term retention.
Boost your team’s performance by exploring our comprehensive guide on sales management best practices, packed with actionable strategies and proven techniques.
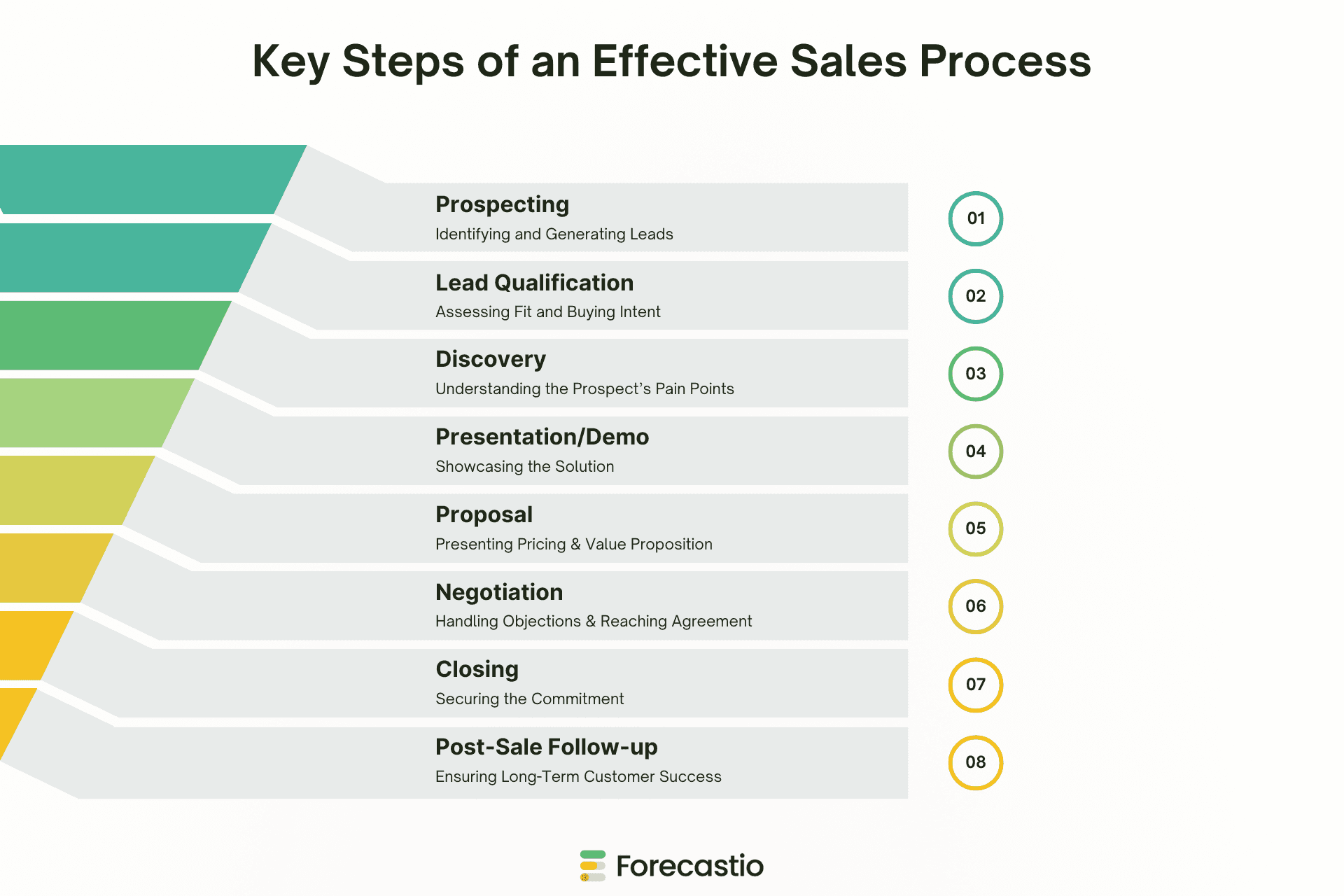
Key Steps of an Effective Sales Process
A structured sales process serves as a roadmap for sales teams, providing clear steps to convert potential customers into long-term clients. Each sales process stage has a unique purpose, guiding sales reps in managing interactions, overcoming challenges, and ultimately closing deals. Below is a breakdown of each stage, including its definition, objectives, best practices, risks, common objections, and potential pitfalls.
1. Prospecting: Identifying and Generating Leads
Definition & Purpose:
Prospecting is the initial phase of the B2B sales process, where sales reps identify and generate high-quality leads who may be interested in the company’s product or service. The goal is to fill the sales funnel with potential opportunities that align with the ideal customer profile (ICP).
Effective prospecting becomes significantly easier when potential buyers can already discover your brand through organic search. Digital Gratified supports SaaS companies by strengthening discoverability through targeted SEO and strategic link building initiatives that improve rankings and drive qualified organic leads.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Leveraging sales tools like CRM systems, AI-driven prospecting, and data analytics.
Using outbound strategies (cold calling, email outreach, industry events) and inbound marketing (SEO, content marketing, referrals).
Targeting decision makers within multiple stakeholders for higher success rates.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
A clear target market and lead qualification framework.
Strong sales messaging and sales pitch templates.
Automation tools for lead sourcing and data enrichment.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Targeting low-intent leads, wasting time and resources.
Common Objections: "I’m not interested," "We’re already using another solution," "Now is not the right time."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Poor lead generation strategy resulting in low-quality leads.
Lack of personalization in outreach.
Engaging the wrong decision-makers who lack purchase authority.
2. Lead Qualification: Assessing Fit and Buying Intent
Definition & Purpose:
Lead qualification determines whether a prospect is a good fit for the company’s offerings. The purpose is to focus sales efforts on potential buyers with genuine interest and the ability to purchase.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Using qualification frameworks like BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timeline) or MEDDIC.
Asking targeted questions to assess buying process readiness.
Filtering out low-potential leads early to improve sales performance.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
A structured qualification checklist and scoring system.
Insights from customer relationship management tools.
A process for identifying red flags, such as lack of urgency or no budget.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Misjudging a lead’s actual intent, leading to wasted effort.
Common Objections: "We’re just exploring options," "We don’t have budget approval yet," "We need internal buy-in."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Engaging with non-decision makers.
Ignoring signs that a lead isn’t a strong fit.
Rushing into the next stage without securing commitment.
3. Discovery: Understanding the Prospect’s Pain Points
Definition & Purpose:
The discovery stage involves meaningful conversations to uncover pain points, challenges, and needs. The purpose is to align the sales strategy with the buyer’s unique problems and priorities.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Asking open-ended questions to understand business goals.
Actively listening and offering insightful solutions rather than just pitching.
Using sales techniques like consultative selling to build trust.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
A structured discovery call framework.
Case studies and testimonials to reinforce credibility.
The ability to articulate value propositions clearly.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Rushing into a sales pitch without deeply understanding the customer’s needs.
Common Objections: "We’re not sure this is a priority right now," "We’ve tried similar solutions before, and they didn’t work."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Lack of differentiation from competitors.
Failure to address key pain points.
Poor communication or lack of personalization.
4. Presentation/Demo: Showcasing the Solution
Definition & Purpose:
This stage is where the sales team presents the product/service as the best solution for the prospect’s problems. The objective is to demonstrate clear ROI and address any lingering doubts.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Customizing demos to reflect the prospect’s business needs.
Highlighting real-world applications instead of just features.
Engaging multiple stakeholders in the presentation.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
Interactive demos and personalized presentations.
Data-driven insights to support the value proposition.
Strong objection-handling techniques.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Delivering a one-size-fits-all pitch that fails to resonate.
Common Objections: "This is too complex," "We’re not convinced of the ROI."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Poorly executed presentations that lack relevance.
Not engaging the full buying committee.
Failing to address competitive differentiation.
5. Proposal: Presenting Pricing & Value Proposition
Definition & Purpose:
At this stage, the sales team presents a formal proposal outlining pricing, value, and deliverables. The goal is to justify the investment and move toward commitment.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Creating clear and concise proposals that highlight ROI.
Addressing budget concerns proactively.
Offering flexible terms where necessary.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
Pricing models that align with customer needs.
Case studies to reinforce credibility.
A follow-up plan to address concerns quickly.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Sticker shock—buyers focus on price rather than value.
Common Objections: "This is beyond our budget," "We need more time to decide."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Lack of clarity in the proposal.
Slow response times in negotiations.
Pricing concerns not addressed effectively.
6. Negotiation: Handling Objections & Reaching Agreement
Definition & Purpose:
Negotiation involves finalizing the deal by addressing concerns, refining terms, and gaining commitment. The objective is to find a mutually beneficial agreement.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Anticipating common objections and having structured responses.
Building trust by demonstrating flexibility without over-discounting.
Ensuring clear communication on terms and expectations.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
Strong negotiation tactics and clear walkaway points.
Competitive analysis to counter objections.
A legal team or contract templates ready to streamline the process.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Losing margin through excessive discounting.
Common Objections: "Can you lower the price?" "We need more favorable terms."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Delays in reaching an agreement.
Failing to address last-minute doubts.
7. Closing: Securing the Commitment
Definition & Purpose:
Closing is the final step where contracts are signed, and the deal is officially won. The goal is to ensure a smooth transition from sales to onboarding.
8. Post-Sale Follow-up: Ensuring Long-Term Customer Success
Definition & Purpose:
This stage ensures long-term customer satisfaction and retention. The focus is on relationship management, support, and future upselling opportunities.
Inbound Sales vs. Outbound Sales
The B2B sales process differs significantly based on whether a company relies on inbound sales or outbound sales strategies. While both approaches aim to convert potential customers into buyers, the way sales teams engage, qualify, and nurture leads varies. Understanding these differences helps businesses optimize their sales process stages to improve sales performance and maximize conversion rates.
Inbound Sales: Engaging Warm Leads Through Marketing Efforts
Definition & Purpose:
Inbound sales is a sales process-based approach where leads initiate contact with the company by showing interest in its products or services. These high-quality leads typically come from content marketing, SEO, webinars, social media, and referrals. The goal of an inbound sales process is to nurture and qualify these prospects before actively engaging them.
What Makes This Sales Process Effective?
Leads are already aware of the brand, making it easier to move them through the sales funnel.
Focuses on educating and nurturing leads rather than aggressively selling.
Utilizes customer relationship management (CRM) systems to track engagement and behavior.
Sales Process Stages in Inbound Sales:
Lead Generation – Attracting potential buyers through marketing efforts.
Lead Qualification – Assessing buying intent based on website activity, downloads, or event attendance.
Discovery – Understanding the buyer’s pain points and needs.
Presentation/Demo – Demonstrating how the solution meets the buyer’s specific requirements.
Proposal & Negotiation – Finalizing pricing and addressing objections.
Closing Deals – Securing commitment and onboarding the customer.
Challenges & Risks in Inbound Sales:
Sales teams depend heavily on marketing efforts to generate demand.
Leads may not be sales-ready, requiring extensive nurturing.
Competition is high, as inbound leads often explore multiple solutions.
Common Objections in Inbound Sales:
"I’m just researching options, not ready to buy yet."
"We’re considering other competitors."
"I need approval from our decision-makers before moving forward."
Why Companies Lose Customers in Inbound Sales:
Failing to follow up quickly with inbound leads.
Poor sales and marketing team alignment, leading to misqualified leads.
Lack of personalized outreach, making prospects feel like just another name in the sales pipeline.
Outbound Sales: Proactively Reaching Potential Customers
Definition & Purpose:
Outbound sales is a proactive approach where sales reps directly reach out to potential clients who may not yet be aware of the company or its offerings. This method relies on cold calling, email campaigns, LinkedIn outreach, and attending industry events to generate interest. Since outbound sales targets colder leads, the sales process requires more effort in lead generation, qualification, and trust-building.
What Makes This Sales Process Effective?
Enables sales professionals to engage decision-makers directly instead of waiting for inbound interest.
Allows sales reps to target specific high-value accounts that fit the ideal customer profile (ICP).
More control over sales pipeline volume and velocity.
Sales Process Stages in Outbound Sales:
Prospecting – Identifying high-quality leads that match the target market.
Cold Outreach – Engaging potential buyers through calls, emails, and LinkedIn.
Lead Qualification – Determining if a lead has the budget, need, and authority to buy.
Discovery Call – Learning about the buyer’s challenges and objectives.
Sales Pitch & Presentation – Demonstrating value with tailored messaging.
Negotiation & Closing – Handling objections, finalizing terms, and closing deals.
Challenges & Risks in Outbound Sales:
Requires persistent follow-up to build trust with potential customers.
Higher rejection rates compared to inbound sales.
Cold outreach must be well-researched to avoid being perceived as intrusive.
Common Objections in Outbound Sales:
"I’m not interested."
"We’re already working with another provider."
"I don’t have time to discuss this right now."
Why Companies Lose Customers in Outbound Sales:
Poor targeting, leading to wasted efforts on unqualified leads.
Weak personalization in outreach, making emails and calls feel generic.
Lack of follow-up, allowing potential clients to slip away.
Key Differences Between Inbound & Outbound Sales
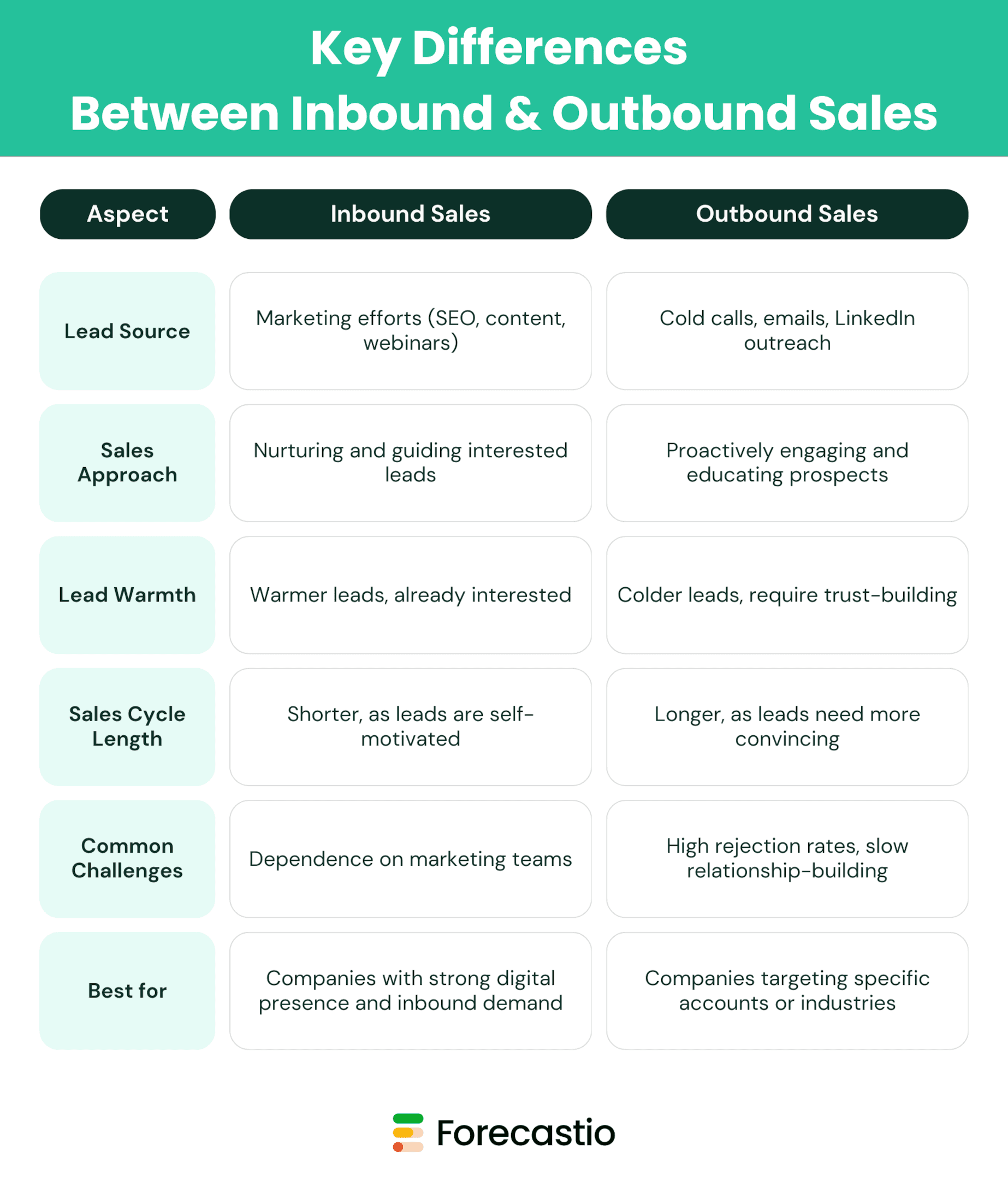
Which Sales Process Is Right for Your Business?
Both inbound and outbound sales have their advantages, and many sales organizations use a hybrid approach to maximize results. The choice depends on:
Your target market: If your audience actively searches for solutions online, inbound sales may be more effective. If they need direct engagement, outbound sales may work better.
Your sales cycle: Shorter cycles may benefit from inbound tactics, while complex, high-value deals often require outbound outreach.
Your team’s expertise: If your sales team excels at consultative selling and handling objections, outbound sales could drive results. If they are skilled at nurturing leads over time, inbound sales might be more effective.
A successful sales process adapts to both inbound and outbound strategies, ensuring sales reps can engage leads effectively at every stage of the buyer's journey. By optimizing both approaches, businesses can increase sales performance, improve lead generation, and achieve consistent revenue growth.
SMB Sales vs. Enterprise Sales
The sales process stages vary significantly between SMB sales and enterprise sales due to differences in decision-making complexity, deal size, and sales cycle length. While SMB sales prioritize speed and efficiency, enterprise sales require a more strategic, relationship-driven approach with multiple stakeholders. Below is a structured comparison:
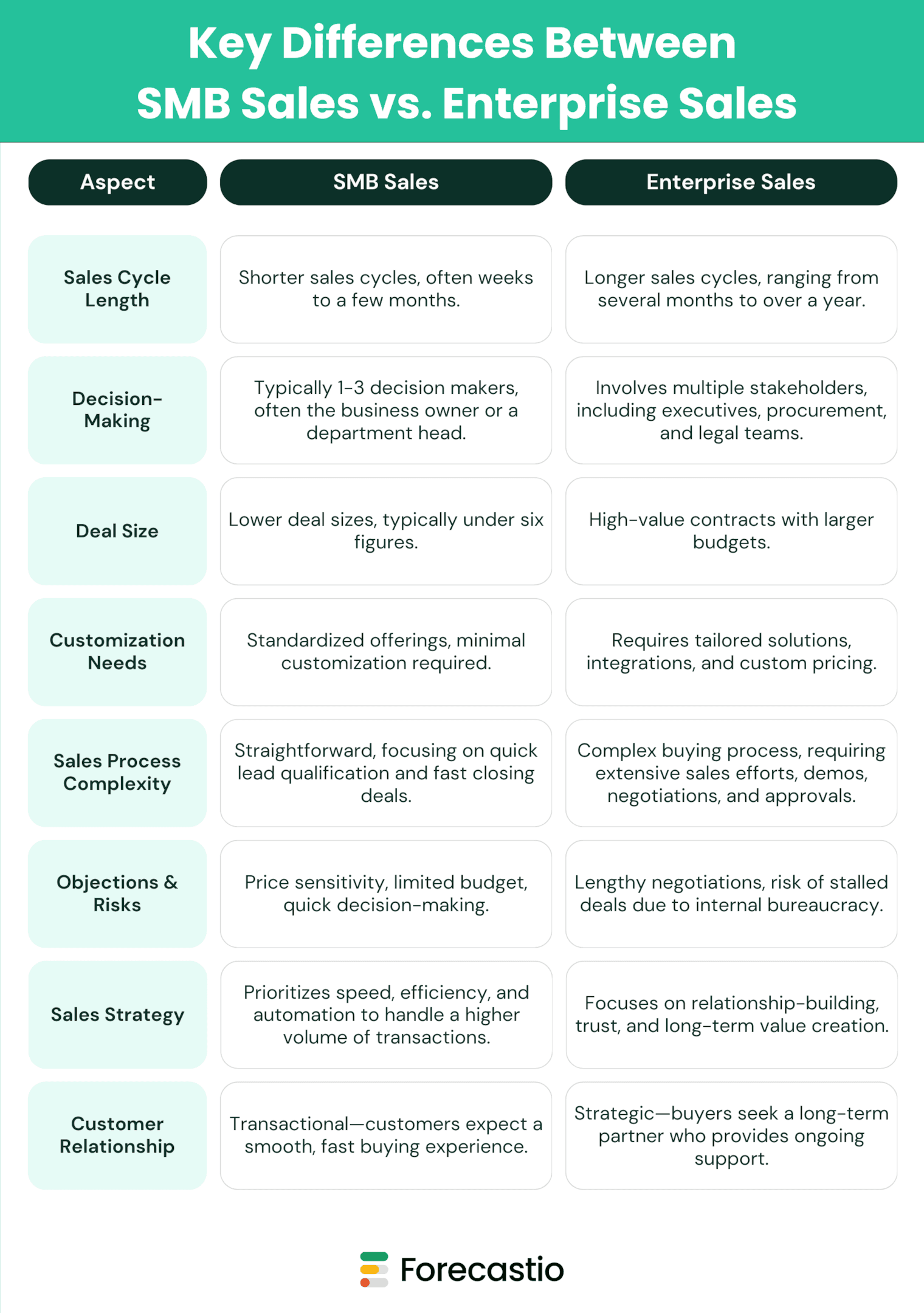
SMB vs. Enterprise Sales Process
The sales process stages differ significantly between SMB sales and enterprise sales, with SMB sales often skipping or shortening steps that are essential in enterprise sales. Below is a comparison of how the sales process typically unfolds in each scenario:
SMB Sales Process (Fast-Paced & Streamlined)
Prospecting & Lead Generation – Identifying potential customers through inbound or outbound efforts.
Qualification – Quickly assessing fit based on budget, need, and urgency.
Sales Pitch or Demo – A brief, standardized presentation of the solution’s value.
Proposal & Pricing Discussion – Sending pricing details, often without heavy negotiation.
Closing the Deal – Fast approval process, often by a single decision maker.
Post-Sale Support & Onboarding – Ensuring a smooth transition to product/service use.
Enterprise Sales Process (Complex & Relationship-Driven)
Prospecting & Targeting – Identifying high-value accounts through ABM (Account-Based Marketing) strategies.
Initial Outreach & Engagement – Personalized sales efforts to connect with multiple stakeholders.
Discovery & Needs Analysis – In-depth discussions to understand pain points and requirements.
Solution Customization & Proof of Concept – Tailoring the offering, sometimes providing pilot programs or case studies.
Formal Proposal & Negotiation – Detailed pricing discussions, legal reviews, and procurement involvement.
Stakeholder Buy-In & Approval Process – Internal meetings and presentations to secure decision-maker consensus.
Closing & Contract Signing – Final approvals, contract negotiations, and agreement execution.
Onboarding & Long-Term Relationship Building – Dedicated customer relationship management, support, and expansion opportunities.
Common Mistakes in a Sales Process
Even a structured sales process can break down due to common pitfalls that hinder sales performance and reduce conversion rates. Below are the most frequent mistakes that sales teams make and how to avoid them.

1. Skipping Qualification
Chasing unqualified leads wastes valuable time and resources, leading to longer sales cycles and lower conversion rates. Without proper lead qualification, sales reps risk engaging with potential customers who lack the budget, authority, or intent to buy.
Solution: Use a defined lead qualification framework (e.g., BANT, MEDDIC) to focus on high-quality leads that fit the ideal customer profile.
2. Lack of Personalization
Generic outreach fails to engage potential clients in a competitive B2B sales environment. Buyers expect solutions tailored to their pain points and business needs.
Solution: Customize messaging based on the prospect’s sales funnel stage, industry, and challenges to increase engagement and trust.
3. Overlooking Follow-ups
Many deals are lost simply because sales reps fail to follow up. A prospect showing initial interest does not guarantee a sale—consistent sales efforts are needed to nurture leads.
Solution: Implement a defined sales process with scheduled follow-ups via phone calls, emails, and LinkedIn outreach to keep leads engaged.
4. Focusing on Features Over Value
A common mistake in the sales process is emphasizing product features rather than demonstrating how they solve the customer’s pain points.
Solution: Align the sales pitch with business impact—highlight efficiency gains, cost savings, and ROI instead of just listing features.
5. Inconsistent Sales Process
Without a structured sales process, different sales reps follow different approaches, leading to inefficiencies, lost deals, and unpredictable sales performance.
Solution: Standardize the sales process stages with a sales playbook, ensuring every deal follows a repeatable, optimized framework.
Key Metrics to Measure Sales Process Effectiveness
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial for evaluating and improving the B2B sales process. These metrics help sales teams optimize their sales efforts, identify inefficiencies, and drive sales performance to achieve consistent revenue growth.
1. Lead-to-Customer Conversion Rate
What It Measures: The percentage of high-quality leads that successfully convert into paying customers.
Why It Matters: A strong indicator of overall sales process effectiveness and the efficiency of lead generation efforts. A low rate may suggest issues in lead qualification, sales messaging, or follow-up strategies.
2. Sales Cycle Length
What It Measures: The time it takes to move a deal from the first interaction to closing the deal.
Why It Matters: A shorter sales cycle often means a more efficient sales process, while longer cycles can indicate bottlenecks, slow decision-making, or ineffective sales techniques.
3. Win Rate
What It Measures: The ratio of won deals to total closed deals in the sales pipeline.
Why It Matters: Reflects how effectively sales reps convert opportunities into customers. A low win rate may indicate issues with sales pitch, objection handling, or targeting the right potential buyers.
4. Average Deal Size
What It Measures: The average revenue generated per closed deal.
Why It Matters: Helps in sales forecasting and strategic planning. Understanding deal size trends allows sales leaders to refine pricing strategies and improve deal qualification.
5. Pipeline Coverage Ratio
What It Measures: The total pipeline value compared to the revenue target.
Why It Matters: Ensures the sales team has enough opportunities in the pipeline to meet sales targets. A low ratio suggests the need for more lead generation efforts, while a high ratio may indicate overreliance on unqualified deals.
Consistently monitoring these KPIs allows sales leaders to fine-tune the sales process stages, improve overall sales efficiency, and achieve sustainable revenue growth.
Summary
An effective B2B sales process is essential for maximizing revenue growth, improving sales efficiency, and increasing conversion rates. A structured B2B sales process helps sales teams operate methodically, ensuring that every stage—from lead generation to closing deals—aligns with the buyer's journey and drives consistent results.
By implementing a defined B2B sales process, companies can create a repeatable, scalable framework that enhances sales performance and improves overall predictability. Tracking key sales metrics, such as lead-to-customer conversion rate, sales cycle length, and win rate, allows businesses to refine their approach and optimize every sales process stage for greater success.
Whether focusing on inbound or outbound sales, targeting SMBs or enterprise clients, a structured B2B sales process ensures that sales professionals close more deals, enhance customer satisfaction, and build lasting business relationships. Companies that continuously refine their B2B sales process eliminate inefficiencies, improve sales techniques, and create a competitive edge in the ever-evolving B2B sales landscape.
Introduction
The B2B sales process has evolved significantly in recent years, driven by more informed potential buyers, extended sales cycles, and increasing market competition. Today’s sales teams must navigate a complex buying process where decision-makers scrutinize every investment, making it essential to adopt a structured sales process that improves efficiency and boosts sales performance.
With tighter budgets and a growing emphasis on measurable ROI, businesses can no longer afford a disorganized selling process. A defined sales process helps sales reps identify and engage high-quality leads, manage the sales funnel effectively, and guide potential clients through the customer journey with precision. By implementing a well-defined sales process, organizations can optimize their sales efforts, increase customer satisfaction, and consistently meet sales targets.
In this article, we’ll explore the key sales process stages, best practices for sales professionals, and actionable strategies for building an effective sales process that accelerates revenue growth and improves deal closing.
What Is a B2B Sales Process?
A B2B sales process is a structured sales process that outlines a clear sequence of steps for sales teams to follow when converting high-quality leads into paying customers. This defined sales process ensures consistency, enhances sales performance, and provides a scalable framework for sales organizations to drive revenue growth.
A well-defined sales process is essential for navigating the complexities of the buyer's journey, especially in B2B environments where multiple stakeholders are involved in the buying process. By aligning sales process stages with customer relationship management best practices, businesses can improve customer satisfaction, optimize sales efforts, and increase their chances of closing deals efficiently.
An effective sales process not only standardizes sales activities but also empowers sales reps with the right sales tools, data, and strategies to engage potential clients at the right time. By adopting a structured approach, sales and marketing teams can better manage the sales funnel, refine their sales pitch, and maximize conversions. And when combined with modern approaches like AI-driven analytics and machine learning sales forecasting, companies gain even deeper insights into pipeline health and future revenue potential.
The Difference Between a Sales Process and a Buying Process
A sales process and a buying process may seem similar, but they represent two distinct perspectives in B2B sales. The sales process is the structured approach that sales teams follow to convert potential customers into buyers, while the buying process (also referred to as the buyer’s journey) focuses on how decision-makers and multiple stakeholders evaluate, compare, and ultimately choose a solution that meets their needs.
Understanding both the sales process and the buying process is crucial because modern B2B buyers are more independent and research-driven than ever before. Today’s sales professionals must go beyond traditional cold calling and scripted sales pitches—they need to engage with potential buyers at the right moments.
By aligning the sales process stages with the buyer's journey, sales teams can increase their chances of closing deals, improve sales performance, and provide a seamless experience that leads to higher customer satisfaction.
Supercharge your growth with our expertly crafted sales improvement strategies, featuring actionable tactics to boost conversions and accelerate pipeline success.
Sales Process vs. Buying Process
To create an effective sales process, it’s essential to recognize how each stage corresponds to the buyer’s decision-making journey. Below is a comparison of the structured sales process and the buying process:

Why Sales Teams Must Align with the Buyer’s Journey
The most successful sales processes are not rigid checklists but adaptable frameworks that align with the buying process. A well-defined sales process ensures that sales reps engage buyers at the right time with relevant messaging, making it easier to guide them through the sales funnel.
By understanding how B2B buyers progress from awareness to purchase, sales leaders can refine their sales strategies, personalize their approach, and build long-term customer relationships that drive revenue growth.
Why an Effective Sales Process Is Important
A well-defined sales process is the foundation of a high-performing sales organization. It provides structure, clarity, and consistency, ensuring that sales reps follow a repeatable approach that maximizes efficiency and improves sales performance.
By implementing an effective sales process, businesses can achieve:
1. Increased Efficiency
A structured sales process helps sales reps focus their sales efforts on high-quality leads, reducing wasted time on low-probability opportunities. By clearly defining sales process stages, reps know exactly when to engage potential customers, how to qualify leads effectively, and which actions will move deals through the sales funnel.
2. Improved Sales Forecasting
A defined sales process creates consistency in sales activities, making it easier for sales leaders and sales managers to predict outcomes with greater accuracy. Reliable sales forecasting enables companies to set realistic sales targets, allocate resources effectively, and anticipate revenue fluctuations. By tracking key performance metrics across the sales cycle, organizations can optimize strategies and make data-driven decisions.
3. Stronger Sales Enablement & Training
For new sales reps, a well-defined sales process serves as a roadmap to success. By following a sales playbook, reps can ramp up faster, understand best practices, and execute proven sales techniques. A structured framework also enhances sales training, equipping teams with the right sales tools to engage potential clients, deliver compelling sales pitches, and navigate complex buying processes.
4. Higher Conversion Rates
An effective sales process ensures that each step is optimized for closing deals. By using a sales process-based approach, sales representatives can nurture potential buyers, overcome objections, and strategically guide them through the buyer's journey. A well-structured selling process reduces drop-off rates and improves the likelihood of successful deal closures.
5. Enhanced Customer Experience & Trust
Aligning sales efforts with customer relationship management best practices ensures that buyers feel supported, informed, and valued. A successful sales process is customer-centric, focusing on solving pain points, addressing concerns, and personalizing interactions. When sales professionals prioritize the needs of potential customers, they build stronger relationships, increase customer satisfaction, and boost long-term retention.
Boost your team’s performance by exploring our comprehensive guide on sales management best practices, packed with actionable strategies and proven techniques.
Key Steps of an Effective Sales Process
A structured sales process serves as a roadmap for sales teams, providing clear steps to convert potential customers into long-term clients. Each sales process stage has a unique purpose, guiding sales reps in managing interactions, overcoming challenges, and ultimately closing deals. Below is a breakdown of each stage, including its definition, objectives, best practices, risks, common objections, and potential pitfalls.

1. Prospecting: Identifying and Generating Leads
Definition & Purpose:
Prospecting is the initial phase of the B2B sales process, where sales reps identify and generate high-quality leads who may be interested in the company’s product or service. The goal is to fill the sales funnel with potential opportunities that align with the ideal customer profile (ICP).
Effective prospecting becomes significantly easier when potential buyers can already discover your brand through organic search. Digital Gratified supports SaaS companies by strengthening discoverability through targeted SEO and strategic link building initiatives that improve rankings and drive qualified organic leads.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Leveraging sales tools like CRM systems, AI-driven prospecting, and data analytics.
Using outbound strategies (cold calling, email outreach, industry events) and inbound marketing (SEO, content marketing, referrals).
Targeting decision makers within multiple stakeholders for higher success rates.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
A clear target market and lead qualification framework.
Strong sales messaging and sales pitch templates.
Automation tools for lead sourcing and data enrichment.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Targeting low-intent leads, wasting time and resources.
Common Objections: "I’m not interested," "We’re already using another solution," "Now is not the right time."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Poor lead generation strategy resulting in low-quality leads.
Lack of personalization in outreach.
Engaging the wrong decision-makers who lack purchase authority.
2. Lead Qualification: Assessing Fit and Buying Intent
Definition & Purpose:
Lead qualification determines whether a prospect is a good fit for the company’s offerings. The purpose is to focus sales efforts on potential buyers with genuine interest and the ability to purchase.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Using qualification frameworks like BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timeline) or MEDDIC.
Asking targeted questions to assess buying process readiness.
Filtering out low-potential leads early to improve sales performance.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
A structured qualification checklist and scoring system.
Insights from customer relationship management tools.
A process for identifying red flags, such as lack of urgency or no budget.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Misjudging a lead’s actual intent, leading to wasted effort.
Common Objections: "We’re just exploring options," "We don’t have budget approval yet," "We need internal buy-in."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Engaging with non-decision makers.
Ignoring signs that a lead isn’t a strong fit.
Rushing into the next stage without securing commitment.
3. Discovery: Understanding the Prospect’s Pain Points
Definition & Purpose:
The discovery stage involves meaningful conversations to uncover pain points, challenges, and needs. The purpose is to align the sales strategy with the buyer’s unique problems and priorities.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Asking open-ended questions to understand business goals.
Actively listening and offering insightful solutions rather than just pitching.
Using sales techniques like consultative selling to build trust.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
A structured discovery call framework.
Case studies and testimonials to reinforce credibility.
The ability to articulate value propositions clearly.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Rushing into a sales pitch without deeply understanding the customer’s needs.
Common Objections: "We’re not sure this is a priority right now," "We’ve tried similar solutions before, and they didn’t work."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Lack of differentiation from competitors.
Failure to address key pain points.
Poor communication or lack of personalization.
4. Presentation/Demo: Showcasing the Solution
Definition & Purpose:
This stage is where the sales team presents the product/service as the best solution for the prospect’s problems. The objective is to demonstrate clear ROI and address any lingering doubts.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Customizing demos to reflect the prospect’s business needs.
Highlighting real-world applications instead of just features.
Engaging multiple stakeholders in the presentation.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
Interactive demos and personalized presentations.
Data-driven insights to support the value proposition.
Strong objection-handling techniques.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Delivering a one-size-fits-all pitch that fails to resonate.
Common Objections: "This is too complex," "We’re not convinced of the ROI."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Poorly executed presentations that lack relevance.
Not engaging the full buying committee.
Failing to address competitive differentiation.
5. Proposal: Presenting Pricing & Value Proposition
Definition & Purpose:
At this stage, the sales team presents a formal proposal outlining pricing, value, and deliverables. The goal is to justify the investment and move toward commitment.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Creating clear and concise proposals that highlight ROI.
Addressing budget concerns proactively.
Offering flexible terms where necessary.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
Pricing models that align with customer needs.
Case studies to reinforce credibility.
A follow-up plan to address concerns quickly.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Sticker shock—buyers focus on price rather than value.
Common Objections: "This is beyond our budget," "We need more time to decide."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Lack of clarity in the proposal.
Slow response times in negotiations.
Pricing concerns not addressed effectively.
6. Negotiation: Handling Objections & Reaching Agreement
Definition & Purpose:
Negotiation involves finalizing the deal by addressing concerns, refining terms, and gaining commitment. The objective is to find a mutually beneficial agreement.
What Makes This Stage Efficient?
Anticipating common objections and having structured responses.
Building trust by demonstrating flexibility without over-discounting.
Ensuring clear communication on terms and expectations.
What Sales Teams Need at This Stage:
Strong negotiation tactics and clear walkaway points.
Competitive analysis to counter objections.
A legal team or contract templates ready to streamline the process.
Risks & Common Objections:
Risk: Losing margin through excessive discounting.
Common Objections: "Can you lower the price?" "We need more favorable terms."
Why Companies Lose Customers at This Stage:
Delays in reaching an agreement.
Failing to address last-minute doubts.
7. Closing: Securing the Commitment
Definition & Purpose:
Closing is the final step where contracts are signed, and the deal is officially won. The goal is to ensure a smooth transition from sales to onboarding.
8. Post-Sale Follow-up: Ensuring Long-Term Customer Success
Definition & Purpose:
This stage ensures long-term customer satisfaction and retention. The focus is on relationship management, support, and future upselling opportunities.
Inbound Sales vs. Outbound Sales
The B2B sales process differs significantly based on whether a company relies on inbound sales or outbound sales strategies. While both approaches aim to convert potential customers into buyers, the way sales teams engage, qualify, and nurture leads varies. Understanding these differences helps businesses optimize their sales process stages to improve sales performance and maximize conversion rates.
Inbound Sales: Engaging Warm Leads Through Marketing Efforts
Definition & Purpose:
Inbound sales is a sales process-based approach where leads initiate contact with the company by showing interest in its products or services. These high-quality leads typically come from content marketing, SEO, webinars, social media, and referrals. The goal of an inbound sales process is to nurture and qualify these prospects before actively engaging them.
What Makes This Sales Process Effective?
Leads are already aware of the brand, making it easier to move them through the sales funnel.
Focuses on educating and nurturing leads rather than aggressively selling.
Utilizes customer relationship management (CRM) systems to track engagement and behavior.
Sales Process Stages in Inbound Sales:
Lead Generation – Attracting potential buyers through marketing efforts.
Lead Qualification – Assessing buying intent based on website activity, downloads, or event attendance.
Discovery – Understanding the buyer’s pain points and needs.
Presentation/Demo – Demonstrating how the solution meets the buyer’s specific requirements.
Proposal & Negotiation – Finalizing pricing and addressing objections.
Closing Deals – Securing commitment and onboarding the customer.
Challenges & Risks in Inbound Sales:
Sales teams depend heavily on marketing efforts to generate demand.
Leads may not be sales-ready, requiring extensive nurturing.
Competition is high, as inbound leads often explore multiple solutions.
Common Objections in Inbound Sales:
"I’m just researching options, not ready to buy yet."
"We’re considering other competitors."
"I need approval from our decision-makers before moving forward."
Why Companies Lose Customers in Inbound Sales:
Failing to follow up quickly with inbound leads.
Poor sales and marketing team alignment, leading to misqualified leads.
Lack of personalized outreach, making prospects feel like just another name in the sales pipeline.
Outbound Sales: Proactively Reaching Potential Customers
Definition & Purpose:
Outbound sales is a proactive approach where sales reps directly reach out to potential clients who may not yet be aware of the company or its offerings. This method relies on cold calling, email campaigns, LinkedIn outreach, and attending industry events to generate interest. Since outbound sales targets colder leads, the sales process requires more effort in lead generation, qualification, and trust-building.
What Makes This Sales Process Effective?
Enables sales professionals to engage decision-makers directly instead of waiting for inbound interest.
Allows sales reps to target specific high-value accounts that fit the ideal customer profile (ICP).
More control over sales pipeline volume and velocity.
Sales Process Stages in Outbound Sales:
Prospecting – Identifying high-quality leads that match the target market.
Cold Outreach – Engaging potential buyers through calls, emails, and LinkedIn.
Lead Qualification – Determining if a lead has the budget, need, and authority to buy.
Discovery Call – Learning about the buyer’s challenges and objectives.
Sales Pitch & Presentation – Demonstrating value with tailored messaging.
Negotiation & Closing – Handling objections, finalizing terms, and closing deals.
Challenges & Risks in Outbound Sales:
Requires persistent follow-up to build trust with potential customers.
Higher rejection rates compared to inbound sales.
Cold outreach must be well-researched to avoid being perceived as intrusive.
Common Objections in Outbound Sales:
"I’m not interested."
"We’re already working with another provider."
"I don’t have time to discuss this right now."
Why Companies Lose Customers in Outbound Sales:
Poor targeting, leading to wasted efforts on unqualified leads.
Weak personalization in outreach, making emails and calls feel generic.
Lack of follow-up, allowing potential clients to slip away.
Key Differences Between Inbound & Outbound Sales

Which Sales Process Is Right for Your Business?
Both inbound and outbound sales have their advantages, and many sales organizations use a hybrid approach to maximize results. The choice depends on:
Your target market: If your audience actively searches for solutions online, inbound sales may be more effective. If they need direct engagement, outbound sales may work better.
Your sales cycle: Shorter cycles may benefit from inbound tactics, while complex, high-value deals often require outbound outreach.
Your team’s expertise: If your sales team excels at consultative selling and handling objections, outbound sales could drive results. If they are skilled at nurturing leads over time, inbound sales might be more effective.
A successful sales process adapts to both inbound and outbound strategies, ensuring sales reps can engage leads effectively at every stage of the buyer's journey. By optimizing both approaches, businesses can increase sales performance, improve lead generation, and achieve consistent revenue growth.
SMB Sales vs. Enterprise Sales
The sales process stages vary significantly between SMB sales and enterprise sales due to differences in decision-making complexity, deal size, and sales cycle length. While SMB sales prioritize speed and efficiency, enterprise sales require a more strategic, relationship-driven approach with multiple stakeholders. Below is a structured comparison:

SMB vs. Enterprise Sales Process
The sales process stages differ significantly between SMB sales and enterprise sales, with SMB sales often skipping or shortening steps that are essential in enterprise sales. Below is a comparison of how the sales process typically unfolds in each scenario:
SMB Sales Process (Fast-Paced & Streamlined)
Prospecting & Lead Generation – Identifying potential customers through inbound or outbound efforts.
Qualification – Quickly assessing fit based on budget, need, and urgency.
Sales Pitch or Demo – A brief, standardized presentation of the solution’s value.
Proposal & Pricing Discussion – Sending pricing details, often without heavy negotiation.
Closing the Deal – Fast approval process, often by a single decision maker.
Post-Sale Support & Onboarding – Ensuring a smooth transition to product/service use.
Enterprise Sales Process (Complex & Relationship-Driven)
Prospecting & Targeting – Identifying high-value accounts through ABM (Account-Based Marketing) strategies.
Initial Outreach & Engagement – Personalized sales efforts to connect with multiple stakeholders.
Discovery & Needs Analysis – In-depth discussions to understand pain points and requirements.
Solution Customization & Proof of Concept – Tailoring the offering, sometimes providing pilot programs or case studies.
Formal Proposal & Negotiation – Detailed pricing discussions, legal reviews, and procurement involvement.
Stakeholder Buy-In & Approval Process – Internal meetings and presentations to secure decision-maker consensus.
Closing & Contract Signing – Final approvals, contract negotiations, and agreement execution.
Onboarding & Long-Term Relationship Building – Dedicated customer relationship management, support, and expansion opportunities.
Common Mistakes in a Sales Process
Even a structured sales process can break down due to common pitfalls that hinder sales performance and reduce conversion rates. Below are the most frequent mistakes that sales teams make and how to avoid them.

1. Skipping Qualification
Chasing unqualified leads wastes valuable time and resources, leading to longer sales cycles and lower conversion rates. Without proper lead qualification, sales reps risk engaging with potential customers who lack the budget, authority, or intent to buy.
Solution: Use a defined lead qualification framework (e.g., BANT, MEDDIC) to focus on high-quality leads that fit the ideal customer profile.
2. Lack of Personalization
Generic outreach fails to engage potential clients in a competitive B2B sales environment. Buyers expect solutions tailored to their pain points and business needs.
Solution: Customize messaging based on the prospect’s sales funnel stage, industry, and challenges to increase engagement and trust.
3. Overlooking Follow-ups
Many deals are lost simply because sales reps fail to follow up. A prospect showing initial interest does not guarantee a sale—consistent sales efforts are needed to nurture leads.
Solution: Implement a defined sales process with scheduled follow-ups via phone calls, emails, and LinkedIn outreach to keep leads engaged.
4. Focusing on Features Over Value
A common mistake in the sales process is emphasizing product features rather than demonstrating how they solve the customer’s pain points.
Solution: Align the sales pitch with business impact—highlight efficiency gains, cost savings, and ROI instead of just listing features.
5. Inconsistent Sales Process
Without a structured sales process, different sales reps follow different approaches, leading to inefficiencies, lost deals, and unpredictable sales performance.
Solution: Standardize the sales process stages with a sales playbook, ensuring every deal follows a repeatable, optimized framework.
Key Metrics to Measure Sales Process Effectiveness
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial for evaluating and improving the B2B sales process. These metrics help sales teams optimize their sales efforts, identify inefficiencies, and drive sales performance to achieve consistent revenue growth.
1. Lead-to-Customer Conversion Rate
What It Measures: The percentage of high-quality leads that successfully convert into paying customers.
Why It Matters: A strong indicator of overall sales process effectiveness and the efficiency of lead generation efforts. A low rate may suggest issues in lead qualification, sales messaging, or follow-up strategies.
2. Sales Cycle Length
What It Measures: The time it takes to move a deal from the first interaction to closing the deal.
Why It Matters: A shorter sales cycle often means a more efficient sales process, while longer cycles can indicate bottlenecks, slow decision-making, or ineffective sales techniques.
3. Win Rate
What It Measures: The ratio of won deals to total closed deals in the sales pipeline.
Why It Matters: Reflects how effectively sales reps convert opportunities into customers. A low win rate may indicate issues with sales pitch, objection handling, or targeting the right potential buyers.
4. Average Deal Size
What It Measures: The average revenue generated per closed deal.
Why It Matters: Helps in sales forecasting and strategic planning. Understanding deal size trends allows sales leaders to refine pricing strategies and improve deal qualification.
5. Pipeline Coverage Ratio
What It Measures: The total pipeline value compared to the revenue target.
Why It Matters: Ensures the sales team has enough opportunities in the pipeline to meet sales targets. A low ratio suggests the need for more lead generation efforts, while a high ratio may indicate overreliance on unqualified deals.
Consistently monitoring these KPIs allows sales leaders to fine-tune the sales process stages, improve overall sales efficiency, and achieve sustainable revenue growth.
Summary
An effective B2B sales process is essential for maximizing revenue growth, improving sales efficiency, and increasing conversion rates. A structured B2B sales process helps sales teams operate methodically, ensuring that every stage—from lead generation to closing deals—aligns with the buyer's journey and drives consistent results.
By implementing a defined B2B sales process, companies can create a repeatable, scalable framework that enhances sales performance and improves overall predictability. Tracking key sales metrics, such as lead-to-customer conversion rate, sales cycle length, and win rate, allows businesses to refine their approach and optimize every sales process stage for greater success.
Whether focusing on inbound or outbound sales, targeting SMBs or enterprise clients, a structured B2B sales process ensures that sales professionals close more deals, enhance customer satisfaction, and build lasting business relationships. Companies that continuously refine their B2B sales process eliminate inefficiencies, improve sales techniques, and create a competitive edge in the ever-evolving B2B sales landscape.
Share:

Alex is the CEO at Forecastio, bringing over 15 years of experience as a seasoned B2B sales expert and leader in the tech industry. His expertise lies in streamlining sales operations, developing robust go-to-market strategies, enhancing sales planning and forecasting, and refining sales processes.
Alex is the CEO at Forecastio, bringing over 15 years of experience as a seasoned B2B sales expert and leader in the tech industry. His expertise lies in streamlining sales operations, developing robust go-to-market strategies, enhancing sales planning and forecasting, and refining sales processes.
Related articles
Pipeline Management
Feb 23, 2026
15 min
Pipeline Management
Feb 23, 2026
11 min
Sales Tools
Feb 23, 2026
15 min
Pipeline Management
Feb 23, 2026
15 min
Pipeline Management
Feb 23, 2026
11 min
Pipeline Management
Feb 23, 2026
15 min
Pipeline Management
Feb 23, 2026
11 min
Sales Planning
Sales Forecasting
Sales Performance Insights
Sales Planning
Sales Forecasting
Sales Performance Insights
Sales Planning
Sales Forecasting
Sales Performance Insights
© 2025 Forecastio, All rights reserved.
Sales Planning
Sales Forecasting
Sales Performance Insights
Sales Planning
Sales Forecasting
Sales Performance Insights
Sales Planning
Sales Forecasting
Sales Performance Insights
© 2025 Forecastio, All rights reserved.
Sales Planning
Sales Forecasting
Sales Performance Insights
Sales Planning
Sales Forecasting
Sales Performance Insights
Sales Planning
Sales Forecasting
Sales Performance Insights
© 2025 Forecastio, All rights reserved.




